Click courses to see descriptions.
All descriptions come from the classes.cornell.edu webpage. The images are pulled from the homeworks and labs of the courses.
Electrical and Computer Engineering
ECE 2100 Introduction to Circuits for Electrical and Computer Engineers
First course in electrical circuits and electronics. Establishes the fundamental properties of circuits with application to modern electronics. Topics include circuit analysis methods, operational amplifiers, basic filter circuits, and elementary transistor principles. The laboratory experiments are coupled closely with the lectures.
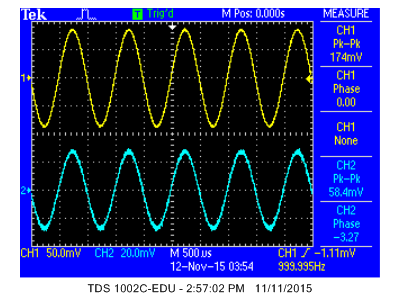
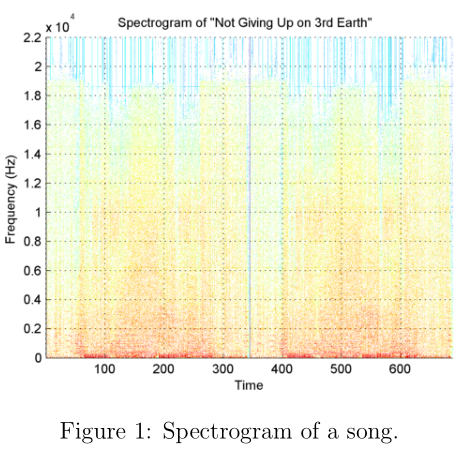
ECE 2200 Signals and Information
Introduction to signal processing. Topics include frequency-based representations: Fourier analysis and synthesis; discrete time linear systems: input/output relationships, filtering, spectral response; analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion; continuous time signals and linear time invariant systems: frequency response and continuous-time Fourier transform.
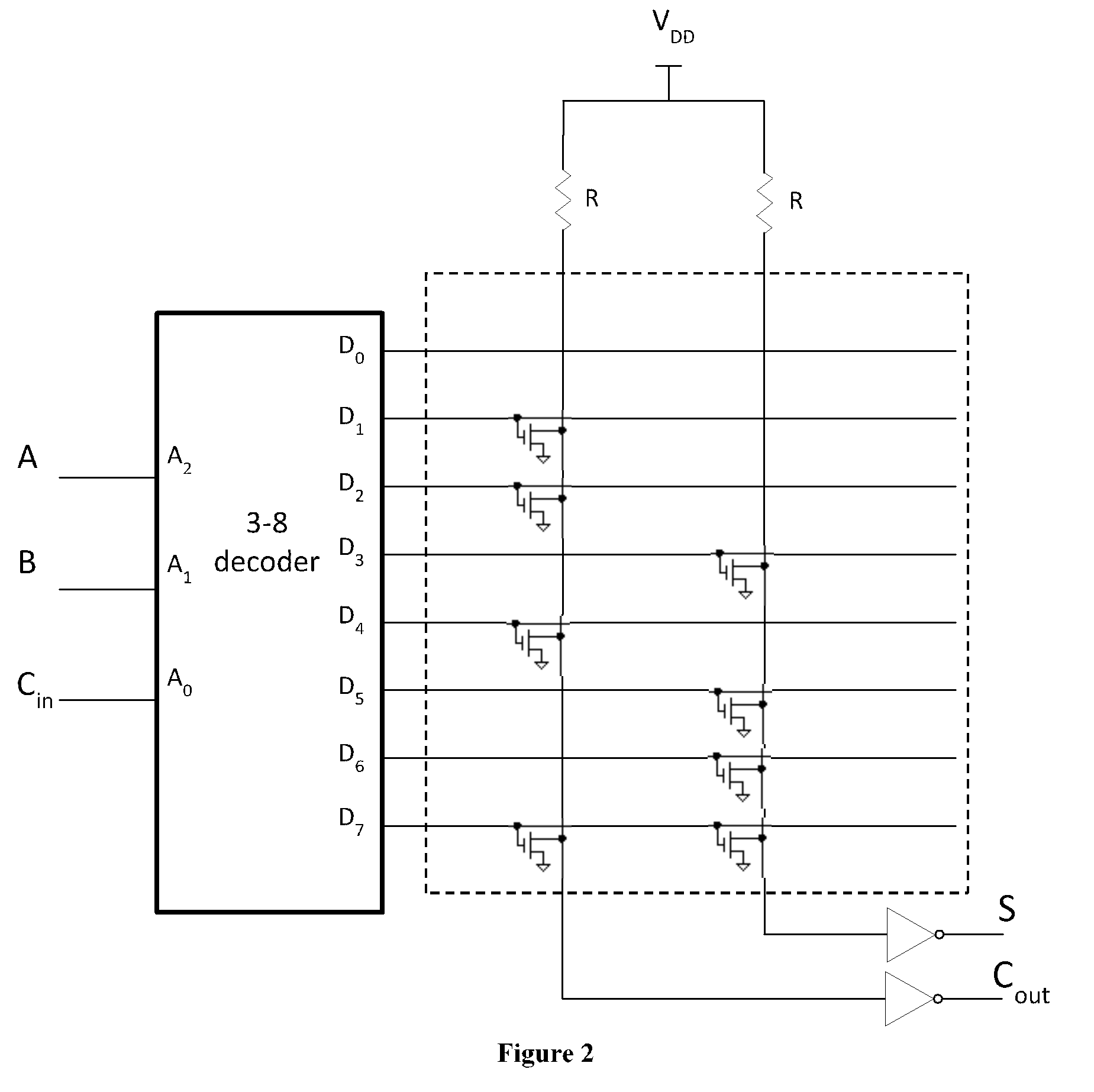
ECE 2300 Digital Logic and Computer Organization
This course provides an introduction to the design and implementation of digital circuits and microprocessors. Topics include transistor network design, Boolean algebra, combinational circuits, sequential circuits, finite state machine design, processor pipelines, and memory hierarchy. Design methodology using both discrete components and hardware description languages is covered in the laboratory portion of the course.
ECE 3100 Introduction to Probability and Inference for Random Signals and Systems
Introduction to probabilistic techniques for modeling random phenomena and making estimates, inferences, predictions, and engineering decisions in the presence of chance and uncertainty. Probability measures, classical probability and combinatorics, countable and uncountable sample spaces, random variables, probability mass functions, probability density functions, cumulative distribution functions, important discrete and continuous distributions, functions of random variables including moments, independence and correlation, conditional probability, Total Probability and Bayes' rule with application to random system response to random signals, characteristic functions and sums of random variables, the multivariate Normal distribution, maximum likelihood and maximum a posteriori estimation, Neyman-Pearson and Bayesian statistical hypothesis testing, Monte Carlo simulation. Applications in communications, networking, circuit design, device modeling, and computer engineering.
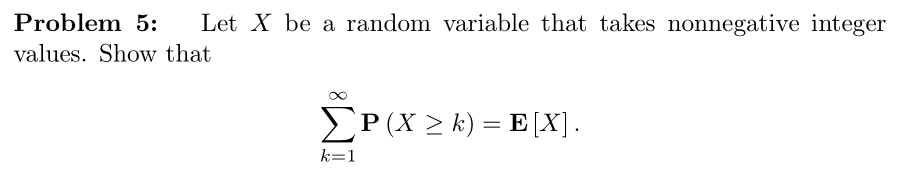
ECE 3140 Embedded Systems
An introduction to the design of embedded systems, with an emphasis on understanding the interaction between hardware, software, and the physical world. Topics covered include assembly language programming, interrupts, I/O, concurrency management, scheduling, resource management, and real-time constraints.
ECE 3150 Introduction to Microelectronics
This is a comprehensive undergraduate level course on microelectronics. Topics covered include basic semiconductor physics, electrons and holes in semiconductors, electrical transport in semiconductors, PN junctions and diodes, photodetectors and solar cells, Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) capacitors, MOS field effect transistors (FETs), bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), large signal and small signal models of electronic devices, single stage amplifiers, multistage amplifiers, differential amplifiers, analog circuit analysis and design, high-frequency models of devices, high-frequency circuit analysis, digital logic and MOS logic devices, complimentary MOS (or CMOS) logic gates, fundamental trade-offs in high speed analog and digital circuit design. The coursework includes labs and a final project.
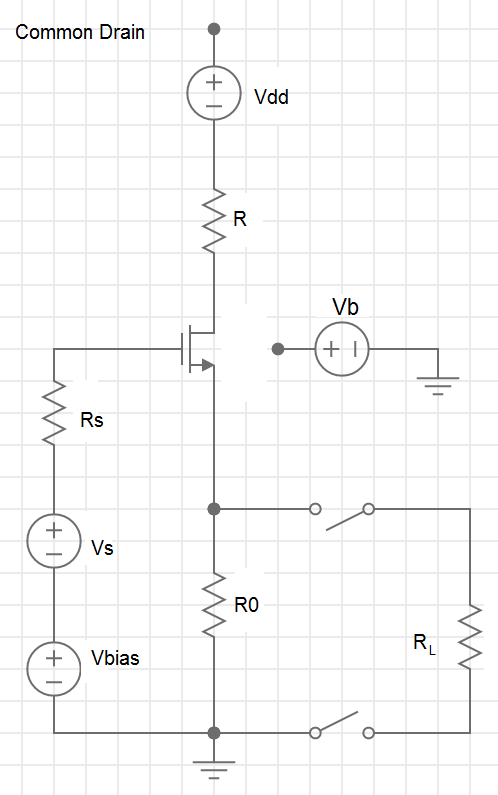
ECE 3250 Mathematics of Signal and System Analysis
Course aims to deepen students' working knowledge of mathematical tools relevant to ECE applications. While the course emphasizes fundamentals, it also provides an ECE context for the topics it covers, which include foundational material about sets and functions; modular arithmetic and public-key cryptography; inner products, orthogonal representations, and Fourier analysis; LTI systems as mappings on function spaces; sampling and interpolation; singular-value decomposition; and, as time permits, an introduction to wavelets and elementary convex analysis.
ECE 3400 Electrical and Computer Engineering Practice and Design
A brief history of electrical and computer engineering, the core subjects that define the field today, the ethical standards of its practice, and instruction in the elements of the process of designing electrical devices and systems. Students engage in experiential-learning design projects in which they will use the design process strategies to function well on a team and to design a system that meets customer needs and electrical engineering constraints.
In this class, a group of 8 students and I had a project of making a self navigating robot that could navigate a maze like that shown in the video below. The robot was able to send a radio signal of its current location as well as the location of an infrared emitter located on the maze.
ECE 4250 Digital Signal and Image Processing
Introduces statistical signal processing. Signal representation and manipulation are covered via correlation and using the DFT/FFT to estimate other transforms; applications of these topics are then covered, including quantization, quantization effects in digital filters, multirate DSP, filter banks, delta-sigma modulation, power spectrum estimation, and introductions to Wiener and Kalman filtering and image processing.

ECE 4300 Lasers and Optoelectronics
Introduction to the operation, physics, and application of lasers. The course covers diffraction-limited optics, Gaussian beams, optical resonators, the interaction of radiation with matter, stimulated emission, rate equations, and laser design. Examples of coherent radiation to nonlinear optics, communication, and leading-edge research are frequently used. Course concludes with a lab where students design and then build a laser.
ECE 4950 Special Topics in Electrical and Computer Engineering: Machine Learning & Pattern Recognition
The course will be devoted to understanding, implementation, and applications of various machine learning primitives. We will cover several unsupervised, and supervised learning techniques. Supervised learning includes regression, support vector machines, decision trees, random forests, naïve bayes, boosting and bagging. Unsupervised learning includes clustering, k-means, k-NN, principal components analysis and other dimensionality reduction methods. We will also cover Mixture of Gaussians, the EM algorithm, and the Viterbi algorithm. We will give particular emphasis on applications in ECE, e.g., text data, hand-writing, music, image, and time series data, and categorical datasets such those in recommendation systems. The course will have a programming component, which will be administered in the form of assignments, or in-class-kaggle competitions.
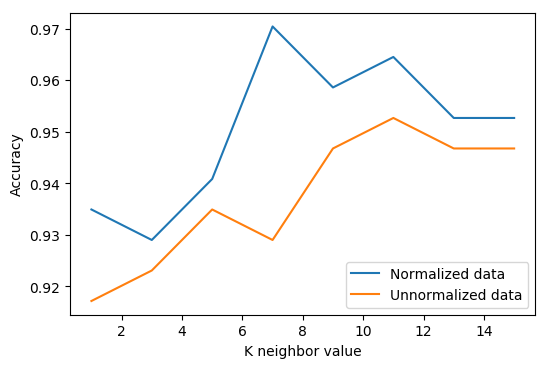
ECE 5470 Computer Vision
Covers computer acquisition and analysis of image data with emphasis on techniques for robot vision. Concentrates on descriptions of objects at three levels of abstraction: segmented images (images organized into subimages that are likely to correspond to interesting objects), geometric structures (quantitative models of image and world structures), and relational structures (complex symbolic descriptions of images and world structures). The programming of several computer-vision algorithms is required.
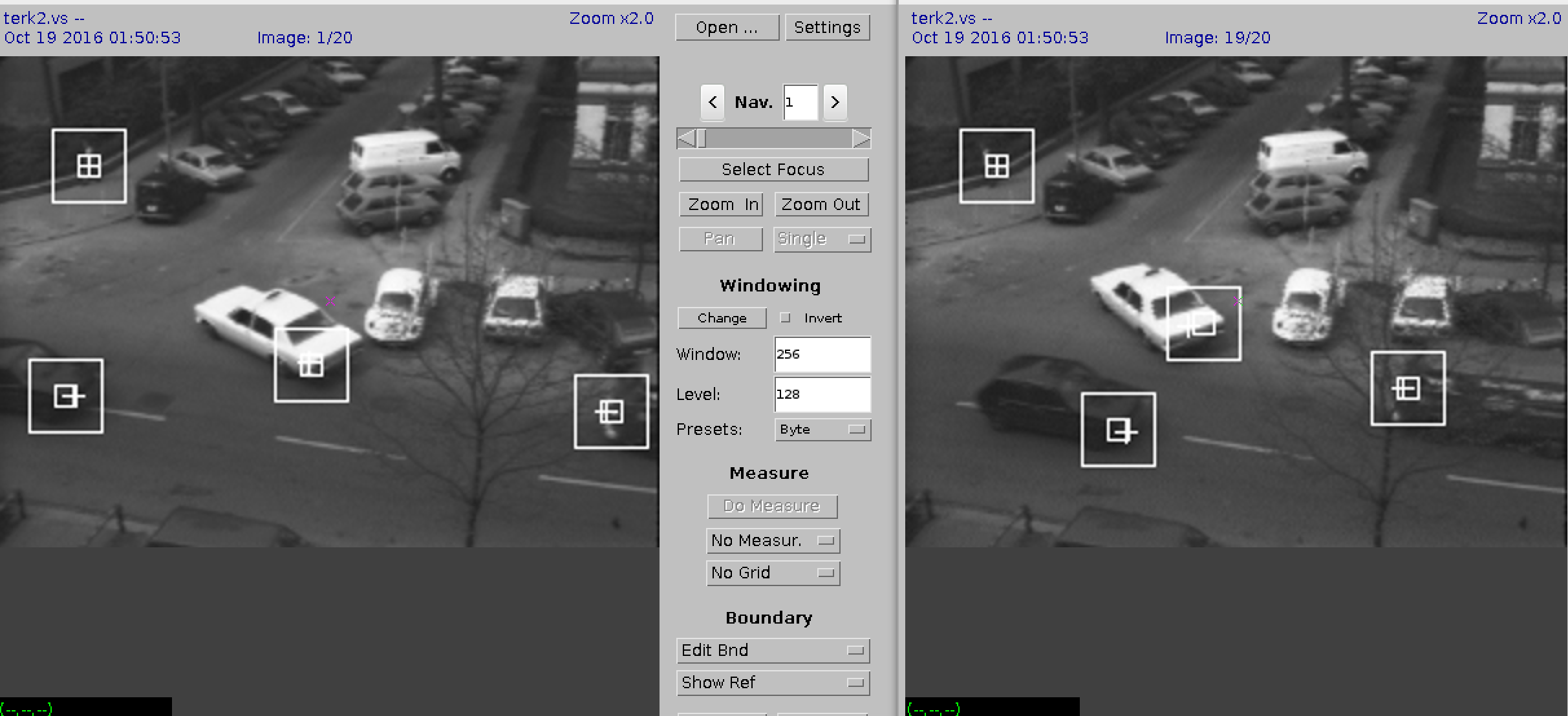
Computer Science
CS 1112 Introduction to Computing Using MATLAB
Programming and problem solving using MATLAB. Emphasizes the systematic development of algorithms and programs. Topics include iteration, functions, arrays, recursion, object-oriented programming, and MATLAB graphics. Assignments are designed to build an appreciation for complexity, dimension, fuzzy data, inexact arithmetic, randomness, simulation, and the role of approximation.
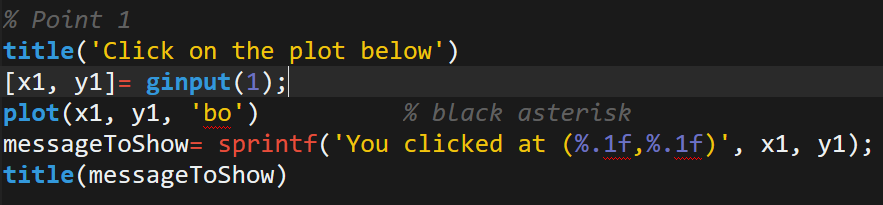
CS 2110 Introduction to Object Oriented Programming
Intermediate programming in a high-level language and introduction to computer science. Topics include program structure and organization, object-oriented programming (classes, objects, types, sub-typing), graphical user interfaces, algorithm analysis (asymptotic complexity, big "O" notation), recursion, data structures (lists, trees, stacks, queues, heaps, search trees, hash tables, graphs), graph algorithms. Java is the principal programming language.
CS 2800 Discrete Structures
Covers the mathematics that underlies most of computer science. Topics include mathematical induction; logical proof; propositional and predicate calculus; combinatorics and discrete mathematics; some basic elements of basic probability theory; basic number theory; sets, functions, and relations; graphs; and finite-state machines. These topics are discussed in the context of applications to many areas of computer science, such as the RSA cryptosystem and web searching.
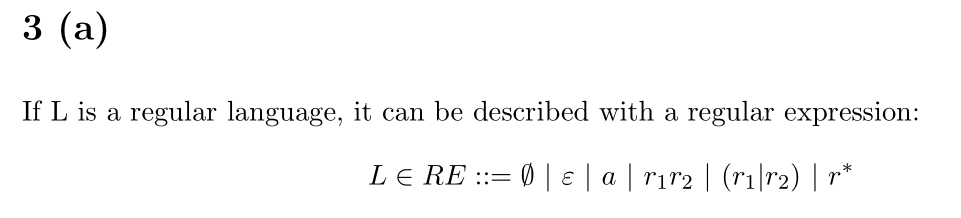
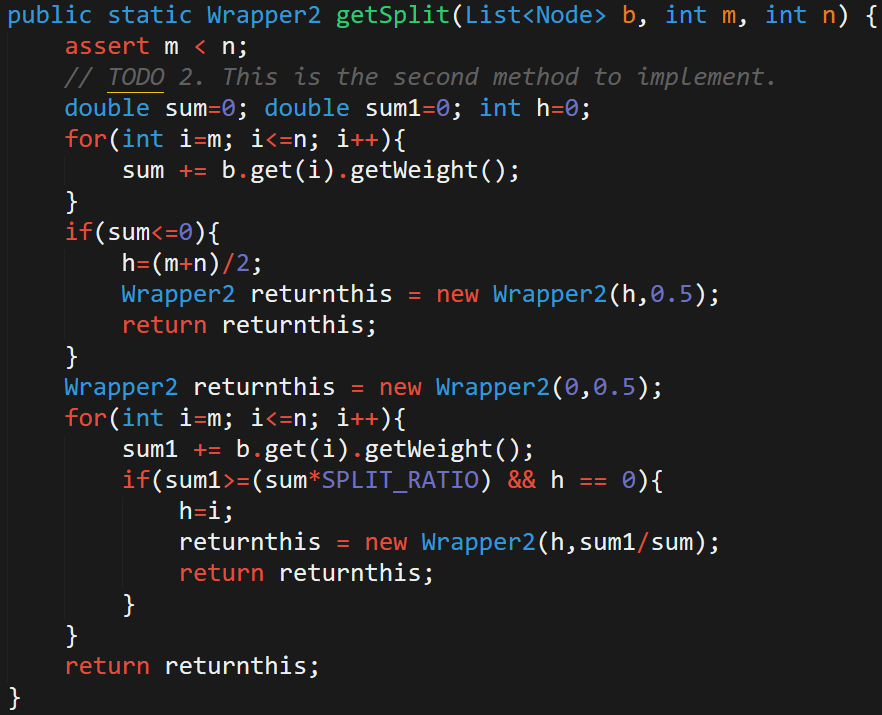
CS 4820 Introduction to Analysis of Algorithms
Develops techniques used in the design and analysis of algorithms, with an emphasis on problems arising in computing applications. Example applications are drawn from systems and networks, artificial intelligence, computer vision, data mining, and computational biology. This course covers four major algorithm design techniques (greedy algorithms, divide-and-conquer, dynamic programming, and network flow), undecidability and NP-completeness, and algorithmic techniques for intractable problems (including identification of structured special cases , approximation algorithms, local search heuristics, and online algorithms).
One dynamic program I wrote for the class is here:
